fat suppression mri
This high signal easily recognized on MRI may be useful to characterize a lesion. In brain MRS scalp and marrow fat can affect the spectra from voxels obtained near the brain surface.

Comparison Of Chemically Selective Fat Saturation And Dixon Techniques Download Scientific Diagram
The disc spaces are preserved and no evidence for degenerative changes is noted.

. In virtually all abdominal MRI examinations suppressing the fat tissue signal is advisable. An update Due to short relaxation times fat has a high signal on magnetic resonance images MRI. With STIR FAT SAT sequences water selective PROSET WATS - water only selection also FATS - fat only selection possible excitation techniques or pulse sequences based on the Dixon method.
For this reason most clinical protocols use fat suppression methods to suppress fat signal and improve visualization of these abnormalities. Fat suppression is the process of utilizing specific MRI parameters to remove the deleterious effects of fat from the resulting images eg. Suppression of fat signal is more uniform and less affected by artifacts than many other techniques.
In musculoskeletal mr imaging fat suppression is specifically used to improve depiction of bone-marrow edema ie lesions confirm or exclude the presence of fat in soft-tissue tumors differentiate high-signal-intensity structures on t1- and t2-weighted images eg protein-rich fluid and methemoglobin eliminate chemical shift artifacts. Rather it consists of several different techniques each meant to address specific needs of various imaging scenarios such as. In MR imaging fat suppression is not one single method.
To suppress the fat signal for a given MR sequence a fat suppression module is typically inserted at the beginning of an otherwise normal MRI sequence. The Dixon method is an MRI sequence based on chemical shift and designed to achieve uniform fat suppression. Identification of fat tissue differentiation from blood clots edema detection enhancement after Gadolinium injection reduction of chemical shift artifacts MR spectroscopy background suppression in MR angiography MRI of breast with fat signal a.
In normal orbits fat suppression was found to be advantageous for imaging the lacrimal gland and the optic nerve. This method is known as outer volume suppression OVS. However small amounts of lipids are more difficult to detect on conventional MRI.
In MRI both spin echo sequences SE and gradient echo sequences GRE may demonstrate chemical shift misregistration or mismapping. Combined use of fat suppression with enhanced MR imaging is essential. Fat suppression is a technique in MRI imaging where fat signals from adipose tissues are suppressed to better visualise uptake of contrast materials of bodily tissues reduce chemical shift artifact and to characterise the type of lesions such as adrenal gland tumors bone marrow infiltration fatty tumors and steatosis by determining the fat content of the tissues.
Eliminating the bright signal. Small FOV imaging eg joints large FOV imaging eg abdomen off-centre imaging eg shoulder and elimination of dark bands from imag- es. Using fat-suppressed T1- or intermediate-weighted sequences 200030 TRTE the optic nerve was recognized by its high signal intensity relative.
Fat suppression is a general term for a collection of MRI techniques designed to specifically alter the signal generated by the magnetic moment of fat hydrogen pro- tons. This is particularly true for standard imaging sequences such as fast spin-echo FSE spoiled gradient echo SPGR and steady-state free precession SSFP. DISCUSSION Among a variety of imaging modalities including ultra-sonography and mammography contrast-enhanced MRI can demonstrate tumor extent and multiplicity and is considered to be a powerful modality for detec-tion and staging of breast cancer.
It has been gaining popularity as it has some advantages over other fat suppression techniques namely. Fat suppression techniques in MRI. In normal orbits fat suppression was found to be advantageous for imaging the lacrimal gland and the optic nerve.
It occurs in the frequency-encode direction where a shift in the detected anatomy occurs because fat resonates at a slightly lower frequency than water. Reducing the signal generated by fat can reveal lesions that would otherwise be masked by fat signal provide insight into tissue fat content or infiltration and mitigate. Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging with fat suppression showing Romanus lesions which appear as a high signal at T9 and T10 levels of the thoracic spine in A and also at T4 on an adjacent slice in B arrows.
And muscle contrast with low-intensity fibrous sheath and fat. There are many applications of fat suppression methods. Fat suppression resulted in a more realistic visual representation of the thickness of optic nerve and muscle presumably the result of increased positive contrast between optic nerve with low-intensity CSF nerve sheath and orbital fat.
Commonly found in Fat suppressed MRI sequences and in MRS. In addition the high signal due to fat may. Fat Suppression in Enhanced Breast MRI 311.
Using fat-suppressed T1- or intermediate-weighted sequences 200030 TRTE the optic nerve was recognized by its high signal intensity relative. The created low signal intensity of fat then contrasts more strongly with the vessels. Fat suppression Suppression of fat tissue is one of the many options that can be used in an MRI sequence.
The most common method to eliminate unwanted fat signal is to place multiple saturation bands over lipid-containing regions. Introduction Fat saturation is an MRI technique used to suppress the signal from normal adipose tissue.

T1 Weighted Brain Mri Axial Section With Fat Suppression Technique Download Scientific Diagram

Fse T2 Weighted Two Point Dixon Technique For Fat Suppression In The Lumbar Spine Comparison With Spair Technique Abstract Europe Pmc

Mri Of The Thoracolumbosacral Spine A Fat Suppression T2 Mri Of The Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Of The Left Knee A Sagittal Fat Sat T2 Weighted Image That Download Scientific Diagram

Effect Of Stir On Fat Suppression A T2 Weighted Fat Saturated Fse Download Scientific Diagram

Incomplete Fat Saturation Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Of The Abdomen And Pelvis A Axial T2 B Fat Suppression Axial T1 Download Scientific Diagram

Axial Mri T2 Weighted Fat Suppressed Sequence Demonstrating The Local Download Scientific Diagram
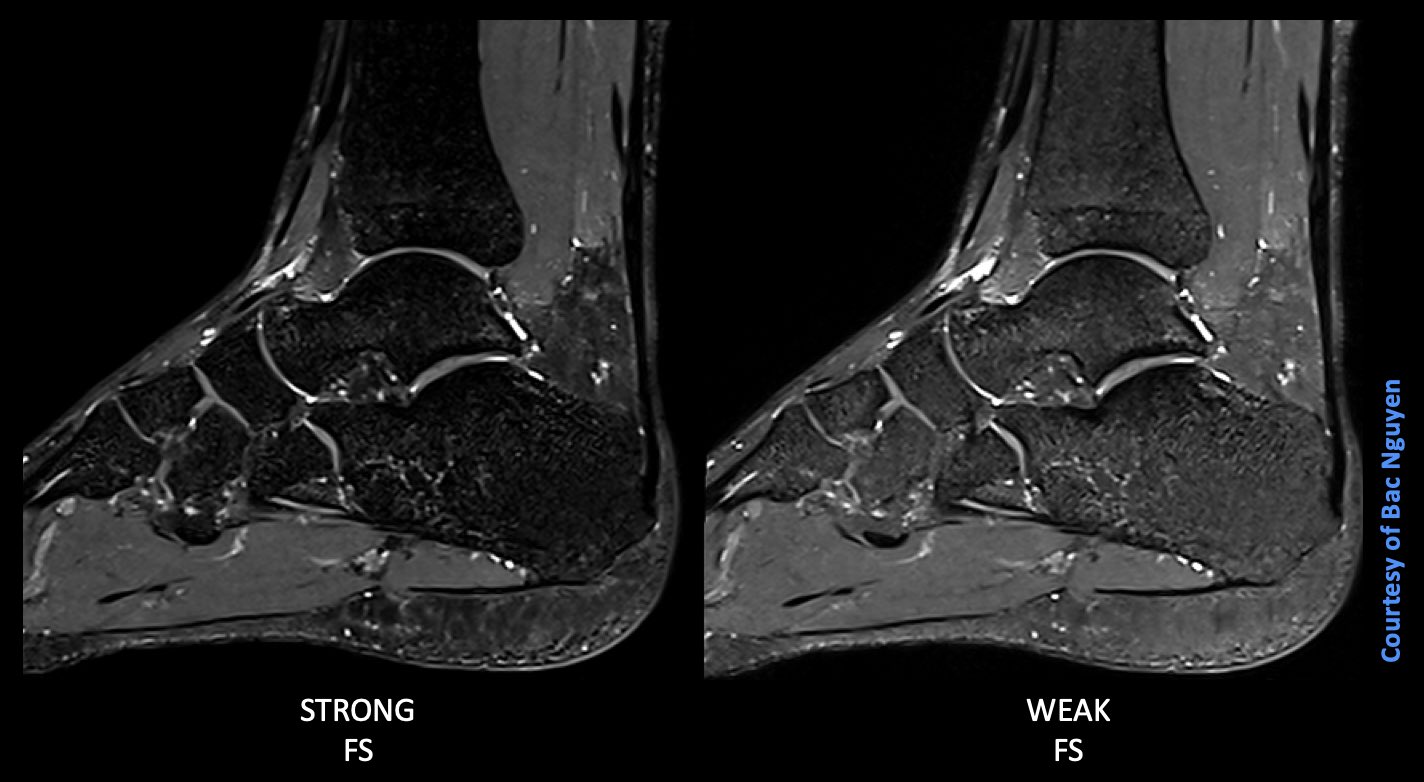
S Magnetic World On Twitter Mr Msk Imaging Fat Saturation 3t For Msk Imaging What Do You Your Radiologists Prefer Either Fat Saturation Strong Or Weak Mode Image Info 3d Pd

Day 3 A Coronal And B Axial T1w With Fat Suppression Mri Scan Of Download Scientific Diagram
Optimal Fat Suppression In Head And Neck Mri Comparison Of Multipoint Dixon With 2 Different Fat Suppression Techniques Spectral Presaturation And Inversion Recovery And Stir American Journal Of Neuroradiology

A An Axial T2 Weighted With Fat Suppression Mri Scan Showing The Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Images T1 And Fat Suppressed Images Showing Transverse Section Of Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Images A And B Fat Suppressed T2 Coronal Images Showing Download Scientific Diagram

The Orbital Fat Suppressed T1 Weighted T1w Magnetic Resonance Imaging Download Scientific Diagram

Why You Should Not Fat Sat All Post Contrast Sequences Radiology Blog Post Radiopaedia Org

Fat Suppressed Imaging Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Inhomogeneous Fat Saturation A Axial T1 Weighted Mr Image 4 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Axial T1 Post Contrast Fat Saturation Sequence Magnetic Resonance Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment